How to Achieve Net Zero Goals through Sustainability Analytics?
An ecosystem, a lifestyle, or a sustainable society that achieves net zero supports itself and its surroundings— the ideology built on the solid fundamentals of sustainability. We need to embrace sustainability because, without it, we won't be able to preserve the diversity of life on Earth, the health of its ecosystems, or our quality of life as human beings. There are signs that we need to address sustainability from all directions and at all scales, from the smallest to the largest. And the understanding and pursuit of economic sustainability—particularly for industrial manufacturing organizations—is at the heart of this transition toward net zero.
Earlier, sustainability was frequently associated with brand development and good governance, but over time, businesses have come to recognize its business levers (operational efficiency, cost savings, etc.), along with regulation and compliance. According to a PwC report, 86% of employees stated they prefer to work for companies that care about the same issues they do, and 73% of customers want to change their mobility behavior to reduce CO2 emissions. Almost all large businesses make net zero commitments as sustainability has taken center stage in boardroom discussions. Manufacturing behemoth Rolls-Royce, for example, unveiled plans to transition to a carbon-neutral company by 2030 and spur net zero transportation. Therefore, one of the most crucial steps toward completing net zero obligations for manufacturing companies is the establishment of net zero facilities.
The term "Smart Manufacturing" comes into the picture and plays a key role in attaining net zero goals through sustainability solutions. The idea of smart manufacturing makes use of recent advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Cloud Computing (CC), and the Internet of Things (IoT). Manufacturing organizations implement these methods and ideologies to overcome the severe non-renewable energy deficit. Many manufacturing sectors emphasize sustainability at every production stage, from procuring raw materials to trash recycling. By committing to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), major organizations have pledged to use minimal to no use of non-replenishable resources in their pursuit of net zero goals through sustainability analytics and ESG reporting.
Broad challenges while implementing corporate sustainability
There is no one-size-fits-all sustainable business plan. The unique challenges and possibilities that an organization's supply chain, customers, stakeholders, and industry face will influence its sustainability initiatives and ESG reporting. Here are a few sustainability issues that will grow in prominence in the future:
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
360° view of a product's lifecycle
Without traceability and transparency in the supply chain, it is almost impossible to establish a truly sustainable organization. This has been the primary concern about business sustainability. An organization cannot guarantee sustainability without a 360° view of a product's lifecycle from raw materials to the point of sale.
Inclusive and accurate data
The growing need for accurate, reliable, and inclusive data that defines and grants status with fairness and equity to all individuals impacted by a company's reach, not simply those normally represented by geography, is one of the major sustainability challenges in business and across industries.
Leveraging Data for UN Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs)
Any organization's ultimate goal should be to ensure that data can be effectively utilized to meet the UN Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) by leveraging the power of data to change minds, policies, and lives.
Transformation of DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) into DEIA (Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Accessibility)
Many firms' DEI initiatives aim to recruit and retain a diverse workforce while ensuring all workers receive equal pay and treatment. As a result, companies and their employees are becoming more proactive in the battle against institutional and structural racism in response to the growing demands. In addition, corporate stakeholders are looking into proactive approaches to address practices that reveal an ingrained bias in their systems as part of their efforts to end racial disparities in institutions.
One trend that has been gaining traction in addressing corporate sustainability challenges around DEI is how to operationalize strategies that encourage and exploit inclusive innovation within businesses and across supply chains. Along with the previously discussed inclusive data, inclusive innovation aims to ensure access, status, and influence for people who have historically been left out of the mainstream development of new products and services.
Minimizing Scope 3 Emissions
All additional indirect emissions connected to the organization, its value chain, and the corporation are included in scope three emissions. Its operating suppliers' emissions are part of that. Regarding emissions output, scope 3 emissions often have the highest levels. But historically, businesses have chosen to overlook them in favor of the more obvious fixes. While there are many issues to consider when integrating sustainability within a supply chain, Scope 3 emissions are the most challenging to regulate.
Circular Economy Principles
Business strategies based on the circular economy aim to maintain resources in use, minimize waste and pollution, and restore natural systems. As a result, the circular economy is being increasingly advanced by businesses, rewriting how they view some of the largest sustainability challenges we face today, such as climate change, plastic waste, and soil degradation.
Regenerative Agriculture and Nature-Positive Methods
A nature-positive economy places much greater demands on the private sector to minimize harm and take steps to improve the robustness and health of natural systems. Although there are multiple methods for businesses to adopt a nature-positive strategy using sustainability solutions, we identify two key areas for action:
- Investing in ecosystem restoration both within and outside the value chain, going beyond "no-deforestation."
- Adopting regenerative farming methods to develop agricultural systems that replenish soils, protect biodiversity, and capture carbon.
With the help of sustainability analytics, companies can achieve several converging objectives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, preserving biodiversity, and restoring ecosystems thanks to these two sustainability programs.
Establishing Ethical Compliance Regulations
As compliance evolves, it is crucial to use cutting-edge technology to monitor, assess, and uphold morally higher standards. State legislation is critical to the safety field for employees to end any forms of social inequity or hazardous employment practices. Tech innovations can assist businesses, and their suppliers meet these ethical problems throughout the supply chain by combining sustainable AI solutions and ESG reporting. Modern technology makes monitoring issues like child labor, conflict minerals, and human rights norms easier than ever. However, it is still a sizable sector that many organizations must handle.
Don't just Talk the Talk; Walk the Walk
Even while sustainability is a major requirement, it is still challenging to realize it. Organizations frequently vow to monitor their sustainability aspects but never complete the process. It is inadequate to release marketing and PR statements about reaching the established sustainability goals and net zero targets. Instead, enterprises must create a solid workforce culture, lucid policies, and software solutions like sustainability analytics and ESG reporting to monitor their sustainability policies. As a result, organizations will be able to make future decisions regarding sustainability by integrating their operations and developing a comprehensive understanding of their corporate value chains and operations.
ESG: Not just a "buzzword" anymore
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) is an element whose value is on the ascent that enables manufacturing industries to measure inside their supply and value chains. Today, an effective ESG framework reflects an organization's dedication to sustainable growth, as well as how it addresses the sustainable viewpoints of investors, broader stakeholders, customers, suppliers, and the community.
Organizations and investors can only demonstrate that ESG genuinely matters and can benefit the world through data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and processing enormous amounts of ESG data (often unstructured data). The end objective shouldn't only be an annual report that discusses the ESG priorities of a corporation – rather, the capacity for businesses to track and report ESG development promptly, allowing stakeholders and investors to validate it through data analytics.
Business leaders must take a proactive stance to fully incorporate ESG into their operations in light of the fast-paced developments in the ESG space and mounting stakeholder demand for greater sustainability performance. Corporate governance, risk management, strategies, reporting, and other subjects should all be included in this effort. By incorporating ESG into business plans, core organizations can effectively identify market dynamics and keep aware of ESG risks in their value chains and operational processes.
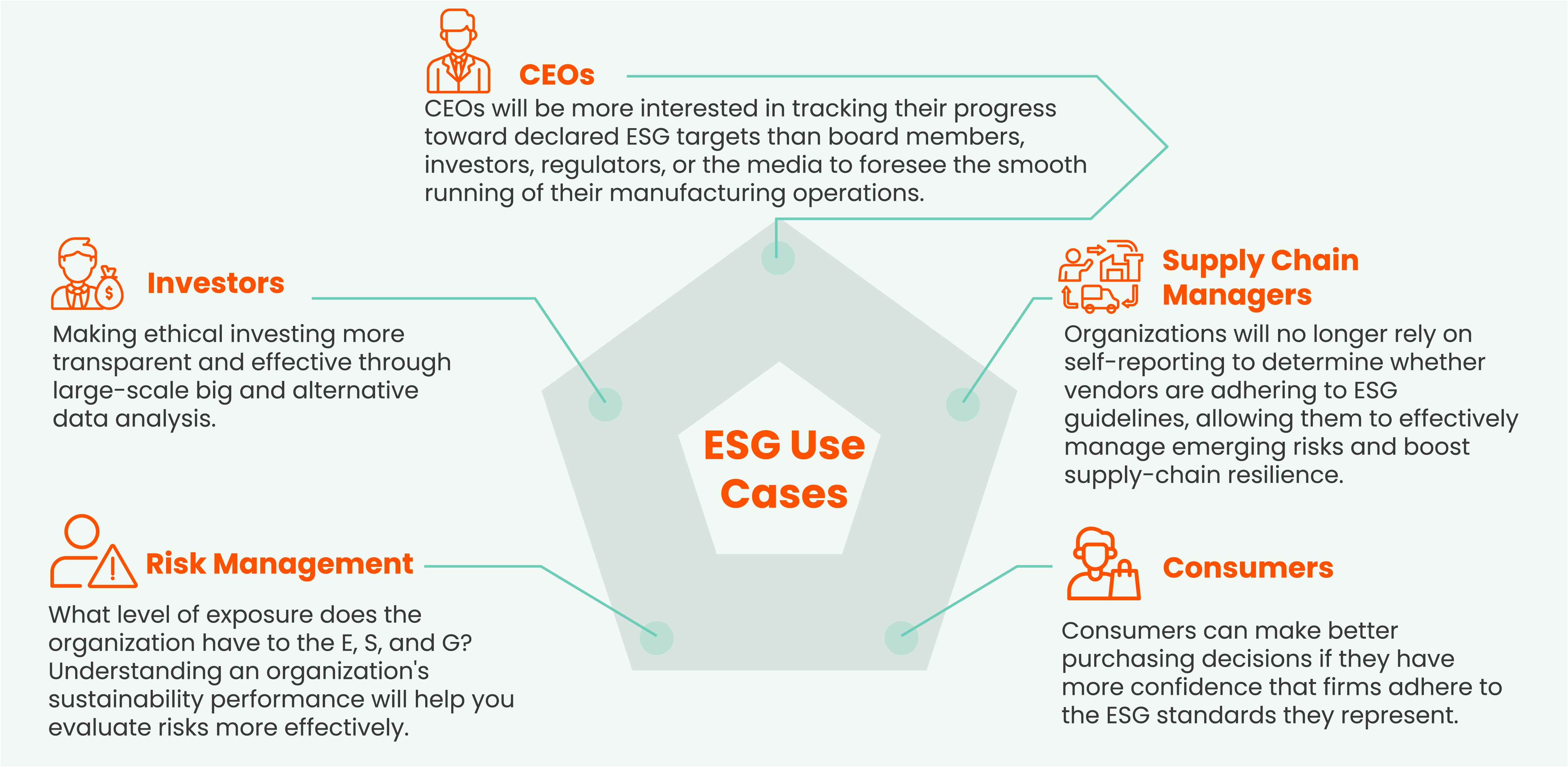
Data analytics in service of ESG
One of the major organizations in Asia and the industrial sector for sustainability is the Indian conglomerate, Tata. Despite decarbonization having substantial costs, Tata sees the short- and long-term impact and ROI differently. For Tata, measuring brand value primarily incorporates sustainability and ESG reporting. Furthermore, Tata's emphasis on sustainability has given the company the potential to attract capital investment and loans. In addition, Tata leadership ordered its group firms to submit thorough evaluations of their ESG compliance as international investors increasingly demand more transparency about the ESG efforts businesses are employing and the returns they would generate.
Tata and other prestigious firms that are working to implement sustainability adhere to the following 3-step process to programmatically enhance ESG and add new dimensions to graph insights:
- Collection
Access and prepare structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from diverse sources for ESG analytics and ML.
- Analysis
Utilize advanced ESG analytics, AI, and ML to develop sustainable models powered by data-driven insights that can be used to assess a company's ESG performance.
- Authentication/Verification
Organizations agree to abide by the regulations using ESG verification as an honor code. AI and ESG analytics enable data teams to glean insights from text and comprehend how several entities affect one another's ESG.
A unified data analytics platform, such as Tredence’s Sustainability Analytics, can help organizations collect information from diverse sources effortlessly and efficiently and store it for accurate analysis in a high-performance data lake. In addition, it will help accelerate the rate at which teams can use ESG analytics, machine learning, and AI at scale to turn data into insights for improved ESG reporting and sustainable decision-making.
Built to Last: A 360° Framework for Automotive and Logistics Sustainability
Identification of businesses that will successfully adapt their business models to address emissions limits is facilitated by the integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects into equity and credit analysis in the automobile manufacturing industry. Many businesses worldwide have embraced the trend towards ESG awareness, ESG reporting, and conducting business ethically, but the automotive sector could be the one driving the most change altogether.
Early adoption by Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) has paved the way for producing environmentally friendly cars that substantially reduce carbon emissions. For example, global automotive colossus BMW emphasizes sustainability by creating hydrogen-fuel cell technology to power its automobiles. By carefully examining their production processes to pinpoint regions where they can make changes, they aim to establish a "sustainable value chain that covers its own needs with recyclates and renewable raw resources, including energy." BMW aims to reduce its CO2 emissions throughout manufacturing by using eco-friendly suppliers and implementing a battery recycling program.
Driving long-term transformation in the automobile industry is the primary goal for many industry players. The challenge is getting the whole automotive value chain on the same page – including manufacturers, dealers, suppliers, service providers, and aftermarket stores - through sustainability solutions.
Encouragement of increased inter-industry collaboration and the use of cutting-edge technology to improve visibility throughout the supply chain are two important ways the sector is addressing these persistent issues. The visibility of the supply chain is essential for future success. Because of this, networks of automotive OEMs and technology enterprises are collaborating to address industry challenges like supply chain issues, secure data management and transfer, electrification of the sector, including vehicles and charging stations, battery lifecycle management, and environmentally friendly business practices to reduce carbon footprints.
Data analytics, ESG analytics, and advanced technologies can give the industry more visibility into supply chains and benefit from a better understanding of product footprints by measuring the environmental impact of products throughout their lifecycles. As more public organizations are expected to assess carbon emissions and report on sustainability goals and key performance indicators (KPIs), the importance of these cutting-edge technology solutions and sustainability analytics is growing.
Applying the framework: From planning to operations
The road to achieving your company's ESG objectives can be challenging, and it isn't always obvious what actions must be taken to accomplish your sustainability and ESG goals. Beginning with a vast collection of diverse data from manufacturers, IoT, news, geospatial, and emissions data sources, ESG analytics first aggregates and processes it.
ESG implementation necessitates the adoption of processes, regulations, and standards. Moreover, it is in sync with the development team members who advocate for tech-enabled ESG rather than just tech-first. Integrating ESG with data analytics or AI/ML allows you to manage your entire data journey with a unified sustainability platform. The following approaches should be taken into account by organizations as they concentrate on implementing more sustainable methods:
Establish a long-term plan for fundamental transformation that accounts for sustainability at every stage.
- Employ data analytics to enhance visibility and transparency to obtain resources sustainably and ethically.
- Plan for sustainability during the design and engineering phases by tracking, measuring, and reducing emissions throughout the product lifecycle using pertinent data.
- Utilize load-optimized logistics strategies to drive growth, cut emissions, and minimize your carbon footprint.
- Utilize resources and machinery in an energy-efficient manner that is secure for the workforce and the environment.
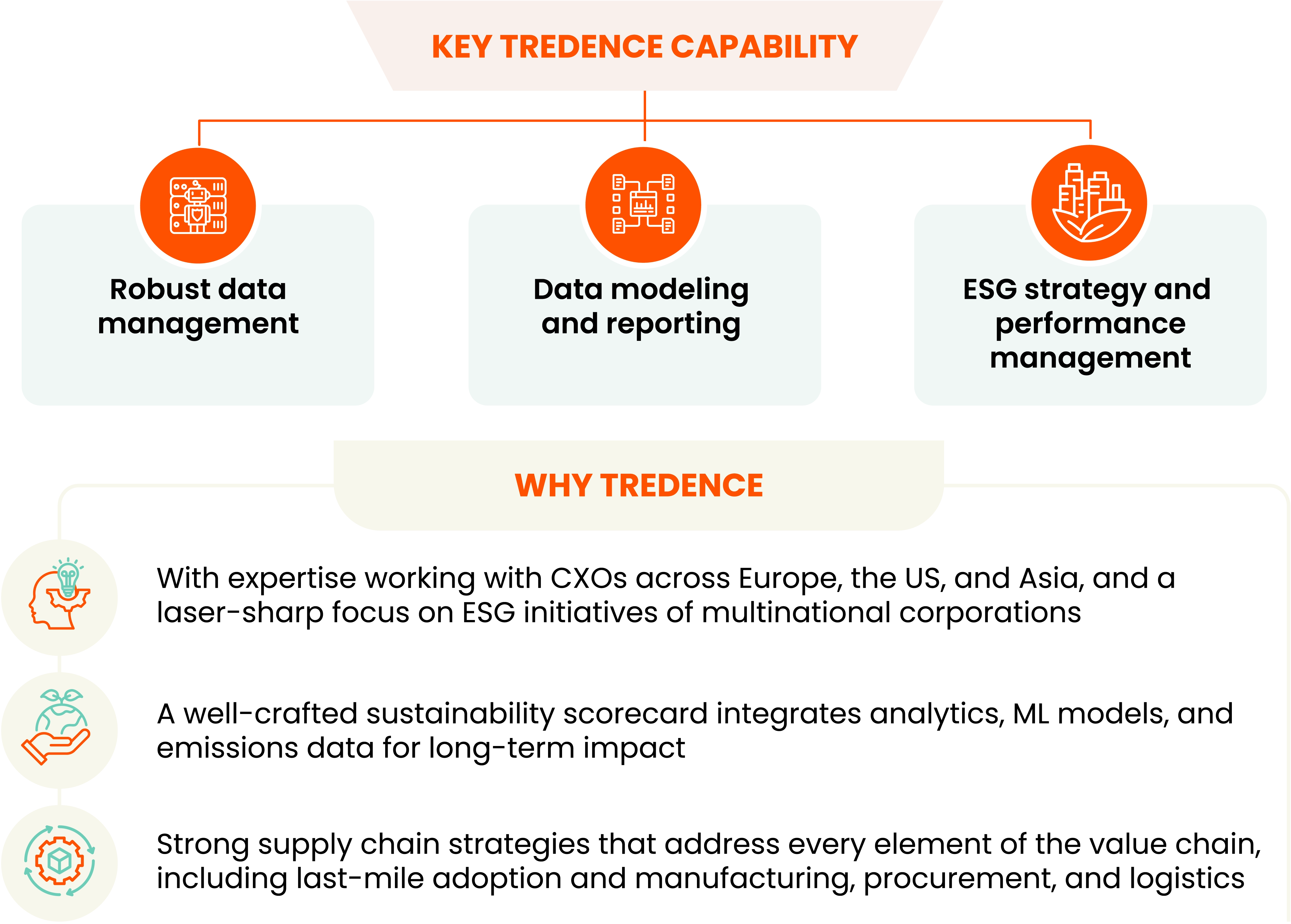
Tredence: Aligning ESG goals with robust sustainability analytics
Technology and data analytics are crucial for managing a sustainable supply chain and accomplishing a company's sustainability objectives. Without the ability to simulate and run what-if scenarios to predict outcomes, enterprises spend much money on projects that, at best, yield bad results. Businesses require a comprehensive understanding of their corporate footprint to affect sustainability initiatives. By tracking their ESG scorecards, recognizing impact opportunities, and adopting strategic action to create the best possible commercial value and long-term sustainability goals, Tredence's sustainability analytics practice assists organizations in taking the lead.
Endgame: The Dawn of a Sustainable Future
Organizational paradigms change due to environmental, social, and governance challenges. As stakeholders, partners, customers, and suppliers demand transparency on carbon and social impact, seek commitments with enhanced ESG priorities, and seek out companies with shared values for partnerships and business arrangements, sustainability is becoming a priority. While also being a wise business decision, it is the right thing to do.
When organizations obtain a real-time view of the various data sets that make up an accurate understanding of ESG, they can evaluate it, individualize it for executives and certain teams, anticipate concerns, rectify them as soon as possible, and establish the groundwork for a positive cycle of resilience. Unified data analytics is essential for achieving the promise of ESG to transform the world.
Tredence, a pioneer in sustainability solutions and services, offers tailored sustainability consulting services and informational assistance for data-driven decisions. If you're looking for a reliable ESG integration and management solution provider to improve your sustainable performance, get in touch with us right away.

AUTHOR - FOLLOW
Editorial Team
Tredence
Topic Tags
Next Topic
De-risk your Supply Chain with data + AI leveraging AWS, Databricks and Tredence
Next Topic




